Amylase is an enzyme, or special protein, produced by your pancreas and salivary glands. The pancreas is an organ located behind your stomach. It creates various enzymes that help break down food in your intestines.
Summary:
A Amylase is secreted by the pancreas into the duodenum where it aids the catabolism of carbohydrates to simple sugars. Damage to the pancreas or obstruction to the pancreatic duct causes the enzyme to enter the blood stream. Elevated levels are found in acute pancreatitis, perforated / penetrating peptic ulcers, paraotitis (mumps). Patients with chronic pancreatic disorders having pancreatic cell destruction do not have high levels as less amylase is produced by the pancreas.
Principle:
A Amylase catalyses the hydrolysis of a 2 – chloro – 4 nitro phenol salt to chloro nitrophenol (CNP). The rate of hydrolysis is measured as an increase in absorbance due to the formation of chloro nitrophenol which is proportional to the a Amylase activity in the sample.
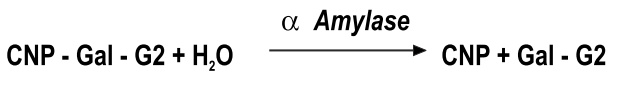
Contents:
| L1. Reagent | 2x10ml , 2x30ml |
Storage / stability:
Contents are stable at 2-8°C till the expiry mentioned on
the label.
Reagent Preparation:
Reagents are ready to use. Do not pipette with mouth.
Sample material:
Serum, Heparinised Plasma, urine.
A Amylase is reported to be stable in the sample for 5 days at 2-8°C. Separate serum from clot as soon as possible.
System Parameters:
| Reaction | Kinetic |
| Wavelength | 405 / (Hg405) / violet |
| Zero Setting | Distilled water |
| lncub. Temp | 37°c |
| lncub. Time | |
| Delay Time | 60 sec. |
| Read Time | 180 sec. |
| No. of read. | 4 |
| Interval | 60 sec. |
| Sample Vol. | 0.02 ml / 0.01 ml |
| Reagent Vol. | 1.00ml |
| Standard Factor | 3954 / 7830 |
| React. Slope | Increasing |
| Linearity | 1000 U/L |
| Units | U/L |
Procedure:
Serum / Plasma Sample:
Pipette into a clean dry test tube labelled as Test (T)
| Addition Sequence | T (37°C) |
|---|---|
| Amylase Reagent ( L1 ) | 1.0 ml |
| Sample | 0.02 ml (20μl) |
Urine Sample:
Pipette into a clean dry test tube labelled as Test (T)
| Addition Sequence | T (37°C) |
|---|---|
| Amylase Reagent ( L1 ) | 1.0 ml |
| Sample | 0.01 ml (10μl) |
Calculations:
a Amylase Activity in U /L (Serum) = M/min.x 3954
a Amylase Activity in U /L (Urine) = M/min.x 7830
Normal value:
The value may vary from lab to lab.
Serum:
- Adult = 19 to 86 U/L
- Newborn = 6 to 65 U /L
Urine:
- Spot Urine : Upto 48 U/l
- 24 hrs Urine: Upto 17 U/l
Amylase Increased Level Is Seen In:
- Acute Pancreatitis and Acute exacerbation of chronic Pancreatitis.
- Pancreatic cyst and pseudocyst.
- Acute alcoholic poisoning.
- Salivary glands diseases like mumps, or duct obstruction or parotitis.
- Maybe in acute cholecystitis, intestinal obstructions.
- Increased in obstruction of the common bile duct, pancreatic duct, or ampulla of Vater.
- Ruptured Ectopic pregnancy.
- Renal failure due to reduced excretion by the kidneys.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis.
- In peritonitis.
- In some of the lung and o to 65 ovarian tumors.
- Alcohol intake.
- May be seen in abdominal trauma, head injury, viral infections, and postoperative patient.
Amylase Level Decreased In:
- Extensive marked destruction of pancreas e.g. Acute Fulminant Pancreatitis.
- Chronic Pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer.
- In pancreatectomy.
- Cirrhosis and severe liver diseases like hepatitis.
- Perforating or penetrating peptic ulcers.
- Toxemia of pregnancy.
- Advanced cystic fibrosis.
Related Articles:
Keywords: amylase,amylase test,serum amylase,amylase blood test,salivary amylase,serum amylase test,amylase normal range,what is amylase,amylase (protein),amylase production,amylase test in hindi,beta amylase,amylase test procedure,blood amylase,alpha amylase,amylase assay,amylase enzyme,amylase meaning,low amylase level,amylase function,amylase and lipase,high amylase level,pancreatic amylase,what is amylase test,amylase test (agd 2020),amylase test and results,amylase production test,amylase high
RELATED POSTS
View all