Intrauterine means “inside the uterus.”
An intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) occurs when a fertilized egg implants and begins to develop inside the uterus, where it is supposed to be. The uterus is the only place where a pregnancy can develop and progress to full term.
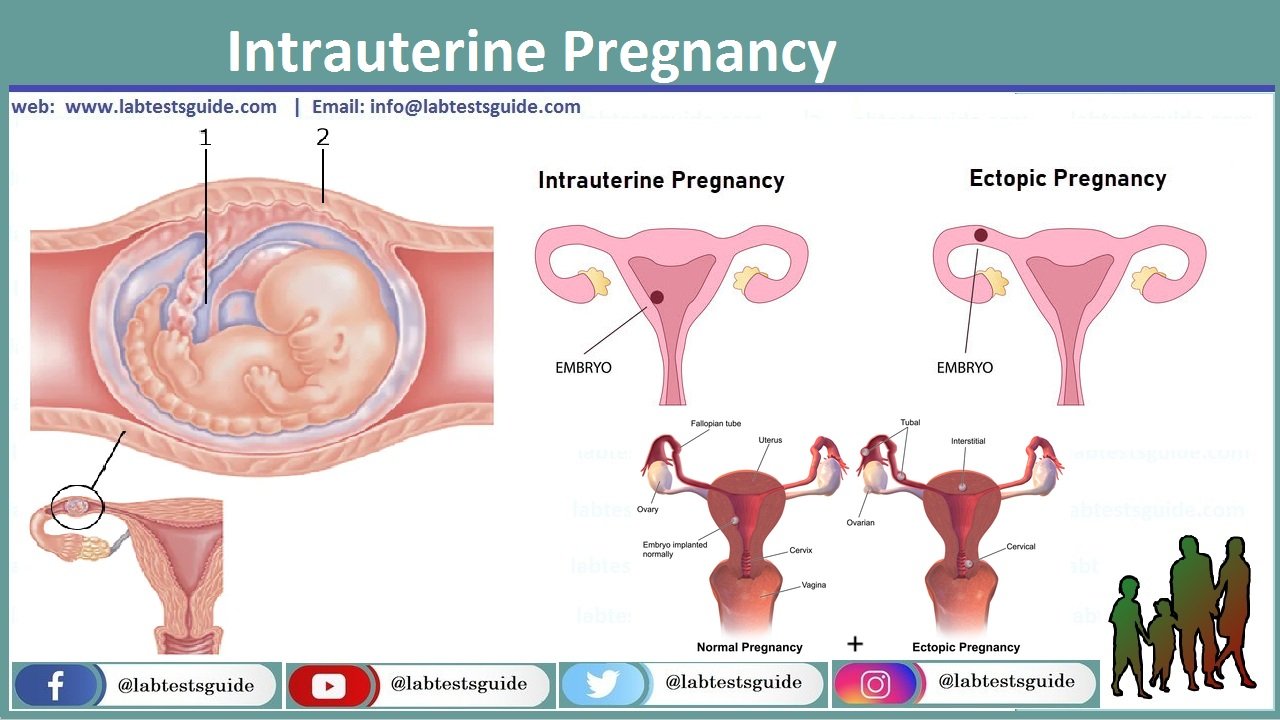
A baby grows inside the mother’s uterus or womb. This is called the intrauterine environment.
An intrauterine device (IUD) is an object that is placed in the uterus to prevent conception and pregnancy.
With spontaneous conception, once an egg is fertilized, it continues to travel down the fallopian tube propelled by finger-like projections called fimbriae into the uterus, where it is likely to implant into the uterine lining.
The uterus is specifically designed to accommodate a growing pregnancy. It has sufficient blood supply to nourish a pregnancy and the ability and flexibility to enlarge with the growing fetus.
In some situations, the fertilized egg implants in places other than the uterus and this is known as an extrauterine or ectopic pregnancy. The fallopian tube is the most common ectopic site, and the tubes are not designed to expand, grow, or host a pregnancy.
A fertilized egg is designed to be naturally invasive. It has a development timeline that is triggered regardless of location. If there is a delay or the inability of the fimbriae to pull a fertilized egg out of the tube, the implantation process can begin in the wrong location.
As the embryo grows and tries to form a placenta, there is inadequate space and the tube does not have the ability to expand, which can cause the tube to burst. This rupture can cause abdominal pain with bleeding and requires immediate medical attention as it can be life-threatening.
RELATED POSTS
View all
