Spontaneous abortion is uninduced embryonic or fetal death or the passage of products of conception before 20 weeks’ gestation. Threatened abortion is cervical non-dilated vaginal bleeding that occurs during this time period and indicates that a miscarriage may occur in a woman with a confirmed viable intrauterine pregnancy. Diagnosis is made using clinical criteria and ultrasound. Treatment is usually watchful waiting for threatened abortion and, if miscarriage has occurred or seems unavoidable, observation or uterine evacuation.
Miscarriage refers to the loss of the pregnancy before 20 weeks of gestation in the absence of elective medical or surgical measures to terminate the pregnancy. The term “miscarriage” is synonymous with and is often used with patients because the word “abortion” is associated with elective termination. “Spontaneous pregnancy loss” has been recommended to avoid the term “abortion” and to recognize the emotional aspects of losing a pregnancy.1 Another emotionally neutral term is “early pregnancy failure”.
Spontaneous abortion, by definition, is the death of the fetus; it can increase the risk of miscarriage in subsequent pregnancies.
Stillbirth and preterm delivery are classified as follows:
- Abortion: death of the fetus or expulsion of products of conception (fetus and placenta) before 20 weeks of gestation
- Stillbirth (stillbirth): fetal death after 20 weeks
- Preterm delivery: passage of a live fetus between 20 weeks and 36 weeks / 6 days
Abortions can be classified as follows (see table Classification of abortions):
- Early or late
- Spontaneous or induced for therapeutic or elective reasons
- Threatened or inevitable
- Incomplete or complete
- Recurrent (also called recurrent pregnancy loss)
- Lost
- Septic
Types of spontaneous abortion
There are several types of spontaneous or spontaneous abortion depending on the factors that influence it:
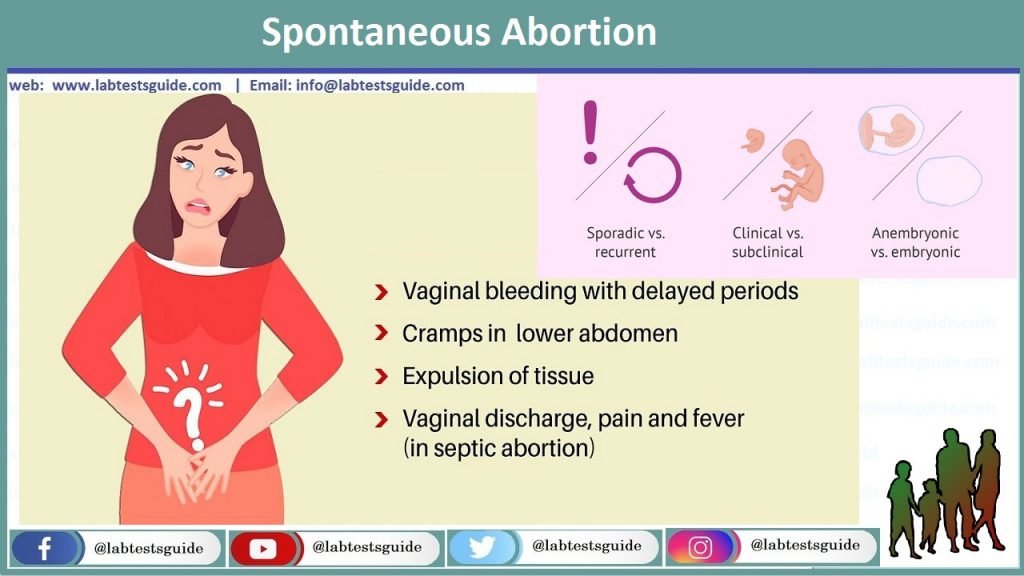
Sporadic versus recurring
Depending on whether it occurs spontaneously as an isolated event or repeatedly in the form of recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL).
Clinical vs subclinical
We consider it clinical when it occurs in the final stages of pregnancy; conversely, it is a subclinical miscarriage if it occurs very early in pregnancy.
Anembryonic vs embryonic
Anembryonic pregnancy or ruined egg is a type of miscarriage in which the gestational sac is empty. An embryonic abortion, on the other hand, refers to an embryo that can be seen, but stops developing.
Complete vs incomplete
We say you are complete if your body is able to expel all the products of pregnancy naturally and incompletely if it does not.
Related Articles:
RELATED POSTS
View all
