Bacteria and viruses are the culprit of many common infections. However, there are differences between the two infectious organisms (Bacteria Vs Viruses).
| Key differences | Bacteria | Viruses |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | They are unicellular organisms found in most habitats on earth. | They are non-living particles consist of genetic material (RNA or DNA) enclosed by a protein core. They are organic structures that interact with living organisms. |
| Where do they grow? | They grow in harsh conditions such as a deep portion of the crust of the earth, radioactive waste, and acidic hot springs. | They are infectious agents that need a host to replicate. |
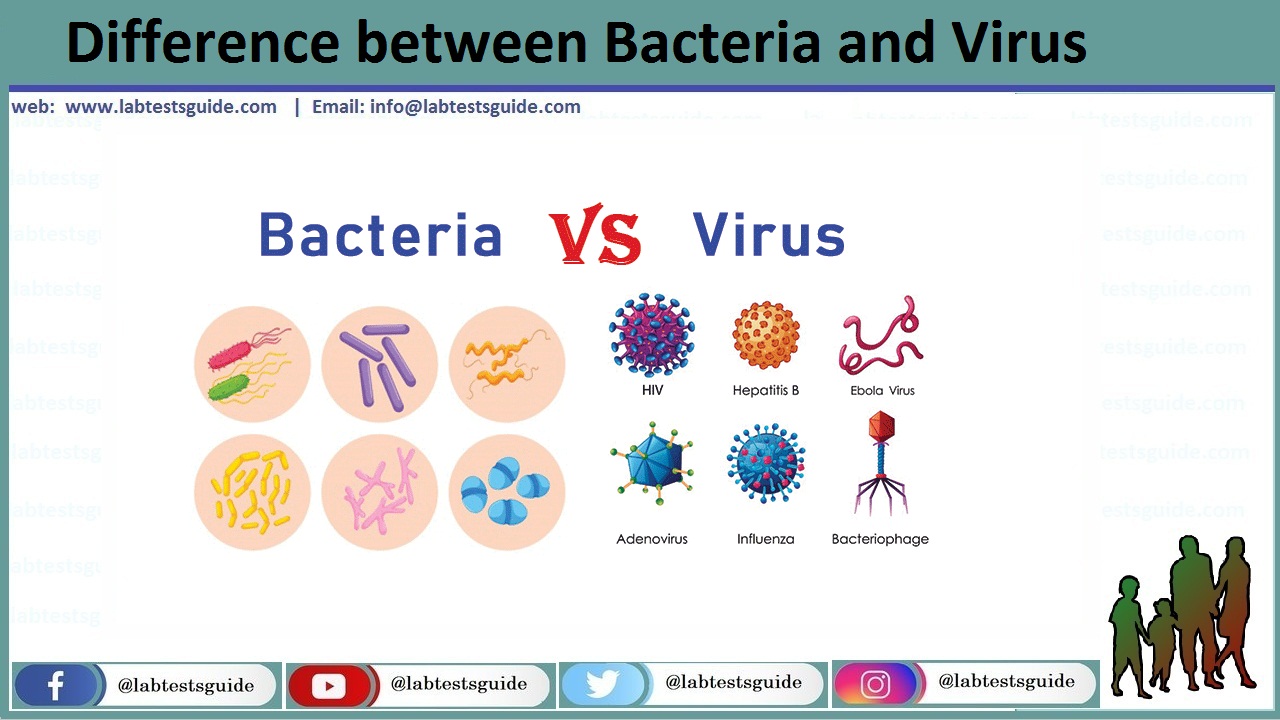
| Classification | They are classified according to their morphology: Cocci – spherical-shaped bacteria Vibrio – comma-shaped bacteria Bacillus – rod-shaped bacteria Spirilla – spiral-shaped bacteria Spirochaetes – tightly coiled bacteria | They are classified according to core content, presence of outer envelope, the structure of capsid, and the way mRNA is produced. |
| What they infect? | They infect all life forms. | They can infect all forms of life including bacteria and archaea. |
| Where can they be found? | They are found in the ecosystem. | They are found in the earth’s ecosystem. |
| How are they visualized? | They are visualized under a light microscope. | They are visualized by means of negative staining. |
| Reproduction requirement | Bacteria can grow and reproduce without a host | Viruses need a host to reproduce as they replicate inside the host. |
| Size | They are large in size (around 1000 nm). | They are small in size (20 to 400 nm) |
| Presence of cell Wall | The cell wall contains peptidoglycan / lipopolysaccharide. | hey don’t have a cell wall but has a protein coat. |
| Number of cells | They are unicellular | They do not have cells. |
| cellular structure | Bacteria are cells and are prokaryotic in nature (displaying characteristics of a living organism) | They are not cells and exist as DNA or RNA particles and enveloped within a protein shell. |
| Presence of ribosomes | They contain ribosomes. | They don’t have ribosomes. |
| Genetic materials | They contain a single circular chromosome. | They have strands of DNA/RNA. |
| Metabolism | They metabolize within the cell. | Metabolism is not present in a viral particle. |
| Reproduction process | The reproduction process takes place through the process of binary fission and conjugation. | They reproduce by invading the host cell and create copies of genetic materials/proteins. They destroy the host cell and release new particles. |
| Utilization of cellular machinery | They possess cellular machinery. | They don’t have cellular machinery. |
| Benefits | They can be categorized as harmful or beneficial. Some bacteria are considered good or healthy, especially those found in the gut. | They are harmful, but some are used for genetic engineering purposes. |
| Ability to infect/Nature of infection | They cause localized infections. | They cause systemic infections. |
| How long the infection last? | They last longer than 10 days. | The duration of the illness varies between 2 and 10 days. |
| Does it cause a fever? | They cause fever. | They may or may not cause fever. |
| Treatment and management | They are treated and managed using antibiotics. | They can be prevented using vaccines. |
| Presence of ribosomes | Yes | No |
| Nucleus | Absent | Absent |
| Presence of enzymes | Present | Present in some |
| Virulence | Yes | Yes |
| Incubation period | It varies depending on the type of bacteria, but usually within 1 to 2 weeks | It primarily depends on what kind of virus causes the disease. The incubation could take a few days to weeks. |
| Characteristics | They are single-celled organisms. Some of them grow as independent single cells while some are multi-cellular fruiting bodies and play an important role in the life cycle. They do not have complex organelles in the cell. They have an internal organization but don’t have a plasma membrane-like other living cells. Bacterial cells have ribosomes (spherical units) where protein assembles from amino acids using the data encoded in the DNA ribosome. | They do not have cellular organelles and cytoplasm. They do not perform metabolic activities. They may only contain DNA or RNA. They can’t contain both. They reproduce at a tremendous amount, but they need a living host to replicate. Many viruses have the ability to mutate. Viruses are like parasites; they use the host cell’s metabolic machinery. They alone cannot grow and divide, they would need a host cell to produce and assemble their viral components. |
| Which is more fatal? | Only about 1% of bacteria cause disease. | The majority of viruses cause diseases. |
| Symptoms/clinical manifestations | The symptoms are confined to a particular infected area of the body as well as the type of bacteria that causes it. Typical clinical manifestations include the following: Swelling Pain Redness Nausea and vomiting Fever | Typical symptoms of viral infections are: Respiratory symptoms like cough and cold Sneezing Tiredness Diarrhea Nausea and vomiting |
| Difference in transmission | Exposure to body fluids Close contact with an infectious person Touching contaminated surfaces Mother to child transmission during childbirth Contact with infected animals/carriers | Exposure to body fluids Close contact with an infectious person Touching contaminated surfaces Mother to child transmission during childbirth Contact with infected animals/carriers |
| Examples of diseases and illnesses | Tuberculosis, strep throat, urinary tract infection | HIV, herpes zoster, influenza, rabies, common cold, and COVID-19 (coronavirus) |
| Common names and strains | Bacillus Coccus Vibrio cholera Rickettsia Staphylococcus aureus Helicobacter bacteria Streptococcus pneumonia | Hepatitis A Virus Papillomavirus Ebola Virus Hanta Virus Rotavirus SARS-CoV SARS-CoV-2 Zika Virus Nairovirus |
| How to prevent the spread of infection? | Hand washing Using alcohol and hand sanitizer Practice good hygiene Avoid touching the face as organisms can enter through the mucus membranes of the face. Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing. Use bleach when disinfecting as it is effective in killing bacteria. | Hand washing Using alcohol and hand sanitizer Practice good hygiene Avoid touching the face as organisms can enter through the mucus membranes of the face. Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing. Use bleach when disinfecting as it is effective in killing viruses. |
| Similarities | Do not have a nucleus Both cause diseases Both microscopic in size Both have virulence | Do not have a nucleus Both cause diseases Both microscopic in size Both have virulence |
Related Articles:
RSS Error: https://www.labtestsguide.com/category/microbiology/feed is invalid XML, likely due to invalid characters. XML error: > required at line 936, column 16
RELATED POSTS
View all
