T-SPOT. TEST FOR MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS
T-SPOT.TB is a type of interferon-gamma release assays (IGRA) used for latent and active tuberculosis diagnosis. Tuberculosis is highly contagious disease spreading through airborne particles containing Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
The disease can be either;
- Latent (dormant) in which patient has no symptoms and tubercle bacilli are present inactively
- Active in which the organism becomes active and the patient shows signs and symptoms of tuberculosis.
- Early detection of the disease is very vital for the treatment to be started and helps to stop the disease from spreading.
- However, current diagnostic tests have many deficiencies. The most commonly employed test is the sputum microscopy which visually identifies the M. tuberculosis but misses some of the cases.
- A more sensitive test is the isolation of bacterial cultures but it takes up to 6 weeks to get the results.
- Both these tests require trained and skilled human resource. The Mantoux test is another diagnostic tool used for detecting exposure to tuberculosis but has certain limitations in those previously vaccinated for TB due to cross reaction with BCG. It has poor sensitivity particularly in immune-compromised groups.
- To overcome these problems, interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs) are used for the diagnosis of tuberculosis particularly latent tuberculosis.
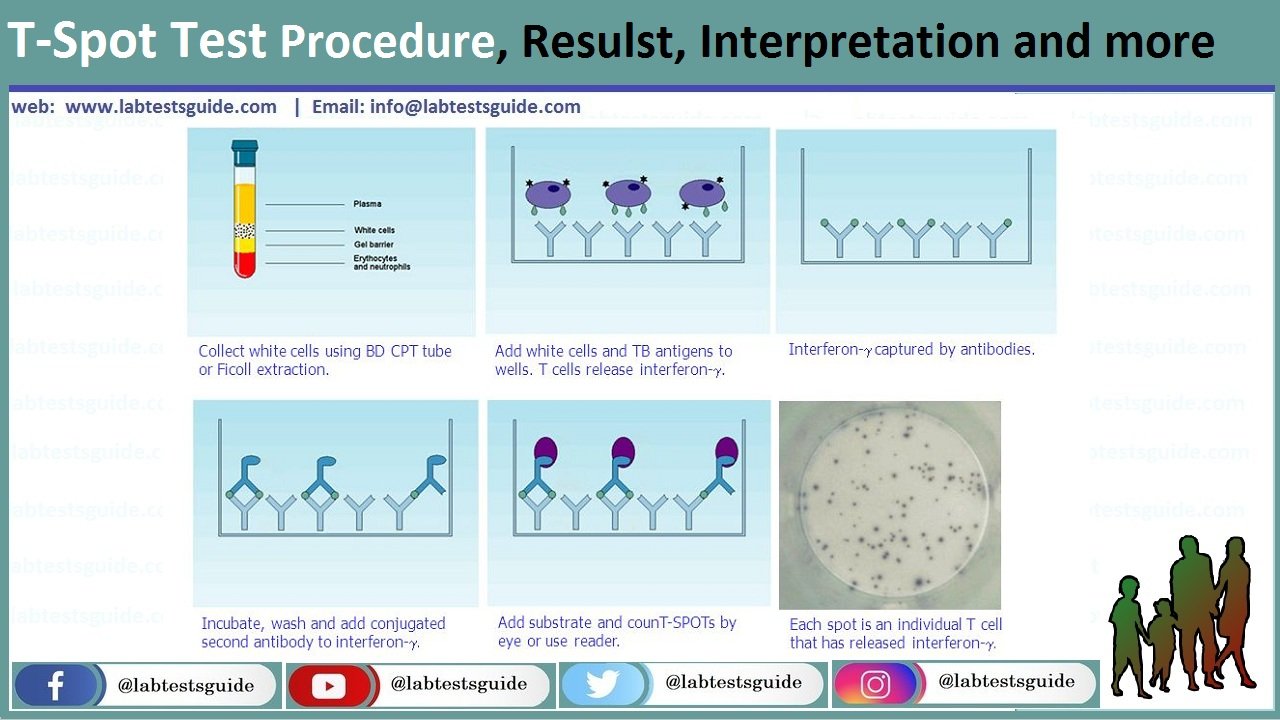
Principle:
The test detects effector T cells that respond to stimulation by M. tuberculosis antigens (ESAT-6, CFP-10) by expressing interferon (INF) gamma. The test is a simplified enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) method which is more sensitive than ELISA. The test does not depend on the production of a reliable antibody response and the TB specific antigens (ESAT-6, CFP-10) also eliminate cross-reactivity to BCG.
Procedure:
- The main steps in the procedure include the separation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from patient’s whole blood.
- PBMCs are then washed and counted before being used in the test.
- After that step incubation is given overnight with the TB antigens which are present in the wells (pre-coated with antibodies to cytokine INF-gamma), the secreted INF-gamma is released by the activated T cells.
- A secondary antibody (conjugated with an enzyme alkaline phosphatase) is added after the washing step.
- After washing a substrate is added, addition of substrate will stop the reaction, and a colored spot production of insoluble precipitate is made, at reaction site showing individual INF-gamma-secreting T cell.
- By counting the number of colored spots, extent of M. tuberculosis effector T cells in the blood can be prepared.
Results:
- Positive >8 spots
- Negative <4 spots
- Borderline 5, 6, or 7 spots
- Invalid
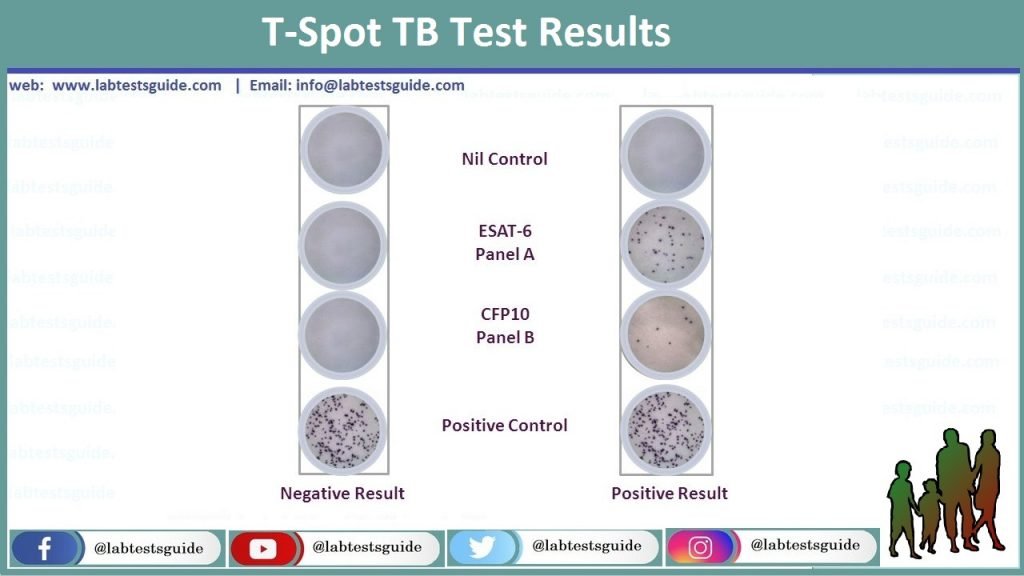
Interpretation of T-Spot.TB:
- A Positive result shows the presence of effector T cells which are reactive to antigens of M. tuberculosis.
- A Negative result shows the absence of effector T cells which are reactive to antigens of M. tuberculosis.
- The test should be interpreted with overall clinical picture.
Related Articles:
RSS Error: https://www.labtestsguide.com/category/microbiology/feed is invalid XML, likely due to invalid characters. XML error: > required at line 936, column 16
RELATED POSTS
View all

