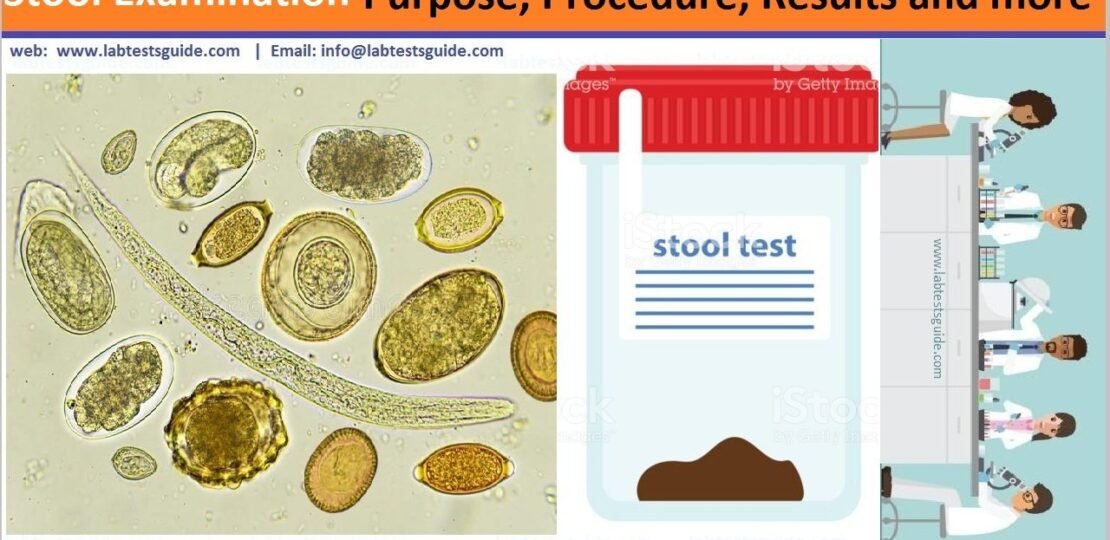
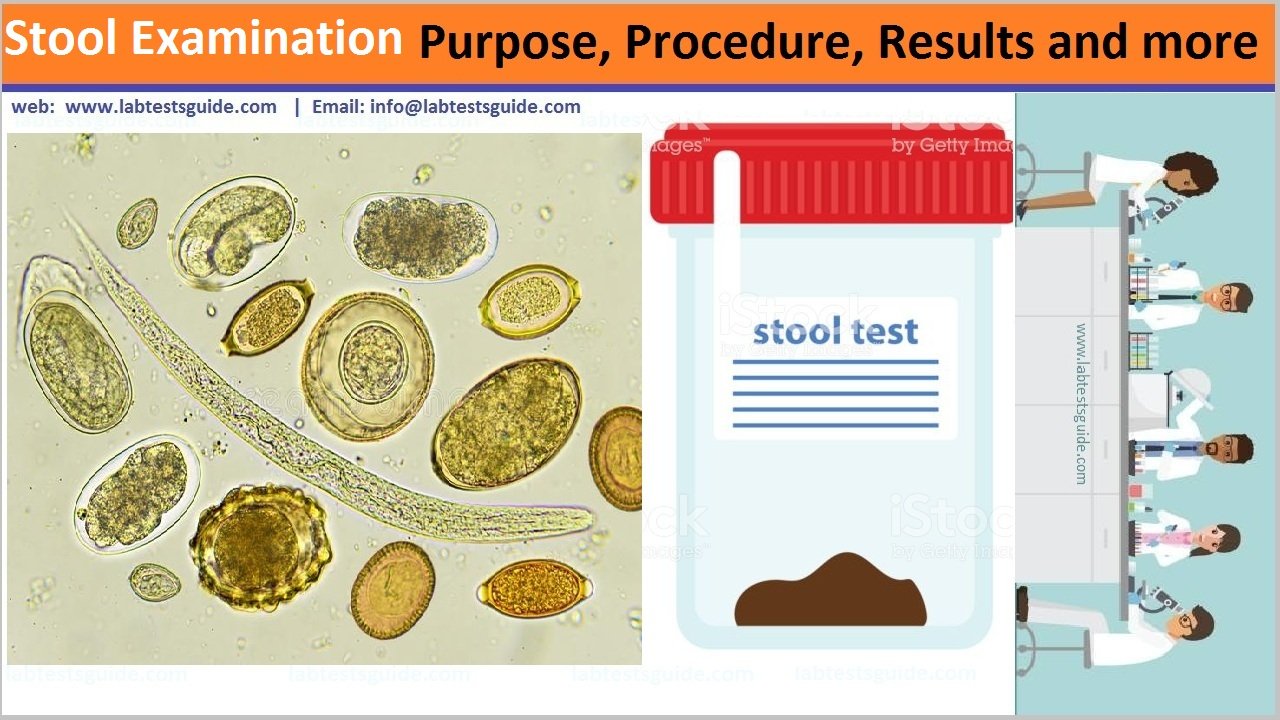
A stool test is a series of tests performed on a stool sample (stool) to help diagnose certain conditions that affect the digestive tract. These conditions may include infection (such as parasites, viruses or bacteria), poor nutrient absorption or cancer.
Also Known as: Stool Analysis, Stool Examination, Stool Test, Fecal Test, Fecal Analysis, Fecal Examination
Related Tests: Stool Occult Blood, Stool Reducing substances, Fecal Examination, Fecal Occult Blood, Fecal Analysis, Stool Test
Why get Tested:
- To evaluate the function and integrity of the GI tract.
- To rule out the presence of WBCs and RBCs.
- To find ova or parasites.
- To see the presence of fat for malabsorption syndrome.
- For screening of colon cancer.
- For asymptomatic ulceration of GI tract.
- Evaluate diseases in the presence of diarrhea and constipation.
- Summary of stool studies are done to evaluate:
- Intestinal bleeding.
- Infestation.
- Inflammatory diseases.
- Malabsorption.
- Different causes of diarrhea.
When to Get Tested:
A doctor may order a stool collection to test for a variety of possible conditions, including:
- allergy or inflammation in the body, such as part of the evaluation of milk protein allergy in infants
- infection, as caused by some types of bacteria, viruses, or parasites that invade the gastrointestinal system
- digestive problems, such as the malabsorption of certain sugars, fats, or nutrients
- bleeding inside of the gastrointestinal tract
Sample Required :
- Fresh stool can be examined immediately to detect moving organisms.
- Stool in 10% formalin can be used for helminths and protozoa.
- The feces in formalin-ethyl acetate are used to concentrate the feces.
- The smallest amount of stool needed for the test is 2 to 5 grams.
Precautions for Sample :
- Advise patients the following for at least 48 hours before stool collection:
- Avoid mineral oils.
- Do not take bismuth.
- Antibiotics such as tetracyclines.
- Antidiarrheal medications that are not absorbent.
- Avoid antimalarial drugs.
- The patient should not have a barium ingestion test before the stool test.
- For Occult blood, stop drugs that contain iron, meat and fish at least 48 hours before collection.
- Warm stools are better for ovules and parasites.
- Do not refrigerate feces for eggs and parasites.
- Feces for ovules and parasites can be collected in formalin and polyvinyl alcohol. These are used as fixative.
- If there is blood or mucus, that should be included in the stool. Because most pathogens are found in this substance.
- Examine feces before giving antibiotics or other drugs.
- Semiformed feces should be examined within 60 minutes after collection.
- Liquid feces should be examined within the first 30 minutes.
- Solid stool should be examined within the first hour of collection.
- Trophozoites degenerate into liquid stools quickly, so you should examine the stool in 30 minutes.
- In the case of cases of constipation, use a non-residual purgative the night before stool collection.
Preservatives of Stool :
- The preservatives for the wet preparation are:
- 10% saline formalin for wet preparation. This is the best preservative since it kills bacteria and preserves protozoa and helminths.
- Sodium formalin acetate.
- Iodine formalin formalin. This is a good preservative for stool collection.
- For staining use polyvinyl alcohol.
- Avoid preservatives for stool culture.
- Usually three parts of the preservatives and one part of the stool.
Examinations:
- Physical Examination
- Chemical Examination
- pH
- Specific Gravity
- Water Contents
- Occult Blood
- Reducing substances
- Porphyrins
- Urobilinogen
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Chloride
- Nitrogen
- Tryspin
- Lipids
- Osmolality
- Microscopic Examination
Normal Stool Findings :
Note: This is a Normal Stool Findings, For Abnormal Stool Findings please study one by one characters.
Physical Examination :
| Characters | Normal values |
|---|---|
| Gross Appearance | May see vegetables, seeds, and fibers |
| Color | Brown |
| Odor | Variable depends upon the bacterial fermentation |
| Consistency | Variable soft to semiformed |
| Amount | 100 to 200 g/day |
| Mucous | Normally absent |
| Blood grossly | Negative |
| Parasites | Negativ |
Chemical Examinations:
| Characters | Normal values |
|---|---|
| pH | Neutral and maybe 7.0 to 7.5 |
| Water contents | 75% |
| Occult blood | Negative |
| Reducing substances | Negative <0.25 g/dL |
| Porphyrins | Corporphyrins = 400 to 1200 µg/day |
| Uroporphyrins = 10 to 14 µg/day | |
| Urobilinogen | 50 to 300 mg/day |
| Sodium | 5.8 to 9.8 meq/day |
| Potassium | 15.7 to 20.7 meq/day |
| Chloride | 2.5 to 3.9 meq/day |
| Nitrogen | <2.5 g/day |
| Trypsin | 20 to 95 U/g |
| Lipids | 0 to 6 g/day |
| Osmolality | 200 to 250 mOsm |
Microscopic Examinations:
| Characters | Normal values |
|---|---|
| WBCs | Negative |
| RBCs | Negative |
| Parasites | Negative |
| Yeast | Negative |
| Bacteria | Negative |
| Viruses | Negative |
| Ova and cyst | Negative |
| Undigested foods | Negative to a small amount |
| Meat fibers, starch | Negative to a small amount |
Related Articles:
RELATED POSTS
View all