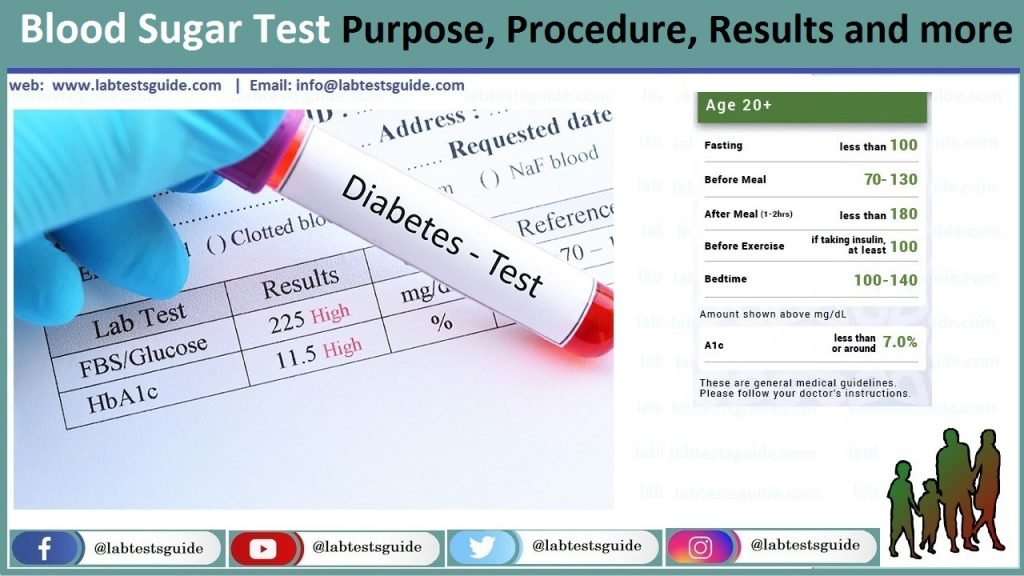
Fasting blood glucose: A test to determine how much glucose (sugar) is in a blood sample after an overnight fast. The fasting blood glucose test is commonly used to detect diabetes mellitus. A blood sample is taken in a lab, physician’s office, or hospital. The test is done in the morning, before the person has eaten. The normal range for blood glucose is 70 to 100 mg/dl.
Also Known as: Fasting Blood Sugar, FBS, Fasting Blood Glucose, Blood Sugar Fasting, BSF, BSL
| Also Known as | BSR, BSF, BSL, Blood Sugar Random, Blood Glucose Random, RBS, Random Glucose, Random Sugar |
| Test Purpose | Describes how blood glucose tests are used, such as to screen for and diagnose prediabetes and diabetes, to detect hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia, and to monitor blood glucose levels over time when treating diabetes |
| Test Preparations | No Need any Preparation |
| Test Components | BSR (Blood Sugar Random) |
| Specimen | 2 ML Plasma From 1 Grey Top (Sodium Fluoride) Tube. |
| Stability Room | 6 Hrs |
| Stability Refrigerated | 72 Hrs |
| Stability Frozen | 1 Week |
| Method | Hexokinase |
| Download Report | Download Report |
Why Get Tested:
- This test is done to diagnose diabetes mellitus.
- This test is also done to evaluate and monitoring of the patient with diabetes mellitus.
- This test is also done to detect and diagnose diabetes and prediabetes and to control high blood glucose (hyperglycemia) or low blood glucose (hypoglycemia)
When to Get Tested:
- when you are older than 45 and every three years.
- When you have risk factors for diabetes.
- when you have symptoms suggesting high or low blood glucose.
- During pregnancy.
Test Preparation Needed :
Recommended that you fast (nothing to eat or drink except water) for at least 10 – 12 hours before having a blood glucose test.
Sample Preparation:
- This test can be done on Serum. The serum should be separated within 30 minutes of collection.
- The serum can be stored at 25° C for 8 hours and 72 hours at 4 °C.
- Oxalate blood can also be used. Preservative sodium fluoride may be added.
- The plasma can be stored at 25 °C for 24 hours (when there is preservative sodium fluoride).
Normal Values:
- Adult = 74 to 106 mg/dL (4.5 to 5.9 mmol/L)
- Children = 60 to 100 mg/dL (3.5 to 5.6 mmol/L)
Raised glucose level (Hyperglycemia) seen in:
- Diabetes mellitus, adult and juvenile.
- Physiological causes.
- Strenuous exercise.
- Strong emotions.
- Shock and burns.
- Infections.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Acromegaly and gigantism.
- Pheochromocytoma.
- Cushing’s syndrome.
- Pancreatic diseases.
- Acute and chronic pancreatitis.
- Pancreatitis due to mumps.
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Hemochromatosis.
- Pancreatic cancers.
- other causes are:
- Cerebrovascular accident.
- Chronic liver disease.
- Chronic renal disease.
- Acanthosis nigricans.
Related Articles:
RSS Error: https://www.labtestsguide.com/category/tests/feed is invalid XML, likely due to invalid characters. XML error: > required at line 490, column 16
RELATED POSTS
View all