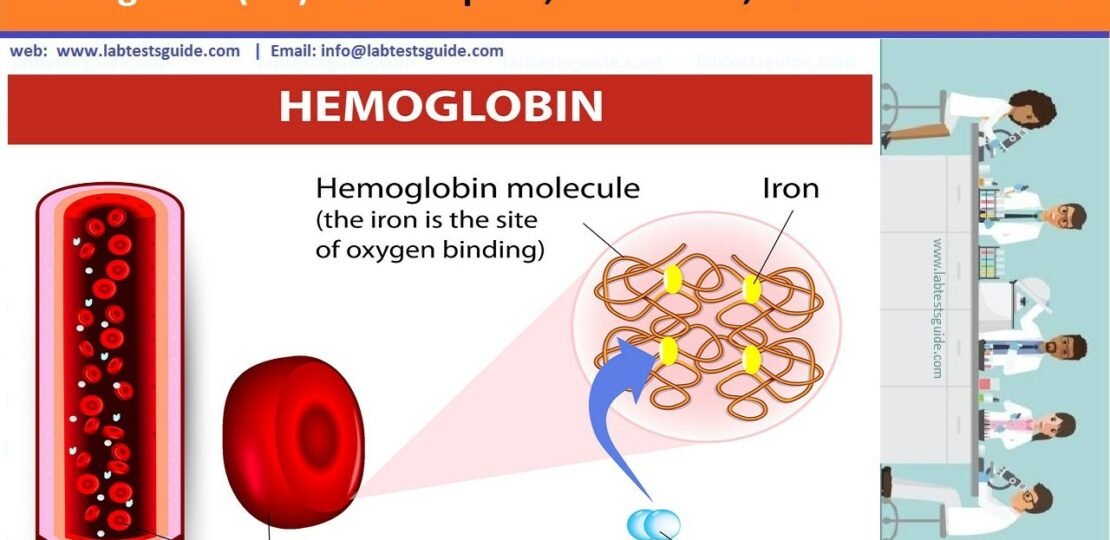
Hgb is a protein produced by your bone marrow that’s stored in red blood cells. It helps red blood cells transport oxygen from your lungs to your body through your arteries.
It also transports carbon dioxide (CO2) from around your body back to your lungs through your veins. Hgb is what makes red blood cells look red.
Also Known As: Hgb, Hb, H and H (Hemoglobin and Hematocrit)
Test Panel: Hemoglobin, Red Blood Cells (RBC), HCT, MCV, MCH, MCHC, Platelets Count, White Blood Cells (WBC), DLC, ESR
Why Get Tested:
- This is done to diagnose anemia.
- It tells the severity of anemia.
- This will monitor the effect of treatment of anemia.
- This is done to evaluate polycythemia.
- This is a part of the complete blood examination.
When to get tested:
Here are a few other reasons your doctor may order an Hgb test:
- You have parents or other family members who have blood disorders, such as sickle cell anemia.
- You have an infection.
- You don’t have enough iron in your diet.
- You’ve lost a lot of blood after surgery or a traumatic injury.
- You’re pregnant.
- You have a medical condition that can affect your Hgb levels.
You don’t need to fast for the Hgb test specifically. You may need to fast — avoiding food or liquids with calories for about 12 hours — if your doctor plans to test the chemistry of your blood at the same time. You should drink plenty of water, however.
Sample Required:
- The blood sample is taken in EDTA.
- Stable 48 hours at 4°C and 24 hours at 23 °C.
Precautions for the sample:
- Avoid Clotting (microcoagules may form).
- Lipemic blood
- In pregnancy, there is a false low Hb due to increased blood volume.
- Gentamicin and methyldopa can increase the Hb value.
- Antibiotics, chemotherapy, aspirin and sulfonamide give low values.
Increased Hb is seen in:
- Polycythemia.
- Polycythemia vera.
- congestive heart failure.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COP).
- After vigorous exercise.
- Hemoconcentration like dehydration, burns, severe vomiting.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Severe dehydration like diarrhea, and burns.
Decreased Hb is seen in:
- Anemia.
- Drugs that cause aplastic anemia.
- Drugs that cause hemolysis ( G6PD deficiency ).
- Immune hemolytic anemia.
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- Thalassemia.
- Pernicious anemia.
- Hemoglobinopathies.
- Liver diseases.and Cirrhosis.
- Hypothyroidism.
- The hemorrhage acute or chronic like bleeding hemorrhoids, or ulcers.
- Malignancies:
- Hodgkin’s disease.
- leukemia.
- Carcinomatosis.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- SLE.
- sarcoidosis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Dietary deficiency
Normal Value:
- Women = 12 to 16 g/dl
- Pregnant women = > 11 g/dl.
- Men = 14 to 17.4 g/dl
Related Articles:
RELATED POSTS
View all