SACE (Serum Angiotensin Converting Enzyme) Test
November 7, 2020 | by fttower.com
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) is an enzyme that converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II helps increase blood pressure by causing the body’s small blood vessels to constrict or narrow.
Also Known As: ACE, Angiotensin-1-Converting Enzyme, Kinase II, Peptidylpeptide Hydrolase, SACE (Serum Angiotensin Converting Enzyme), Sarcoidosis, Serum Angiotensin Converting Enzyme
| Test Name | Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) |
| Test Purpose | Most of the time we uses the ACE level test to monitor a disease called sarcoidosis. |
| Test Preparations | Overnight Fasting Is Preferred. |
| Test Components | ACE |
| Specimen | 2 ML (1 ML Min.) Serum From 1 SST. Ship Refrigerated Or Frozen. Overnight Fasting Is Preferred. |
| Stability Room | 2 Hrs |
| Stability Refrigerated | 1 Week |
| Stability Frozen | 6 Months |
| Method | FAPGG |
| Download Report | Download Report |
Why to Get Tested:
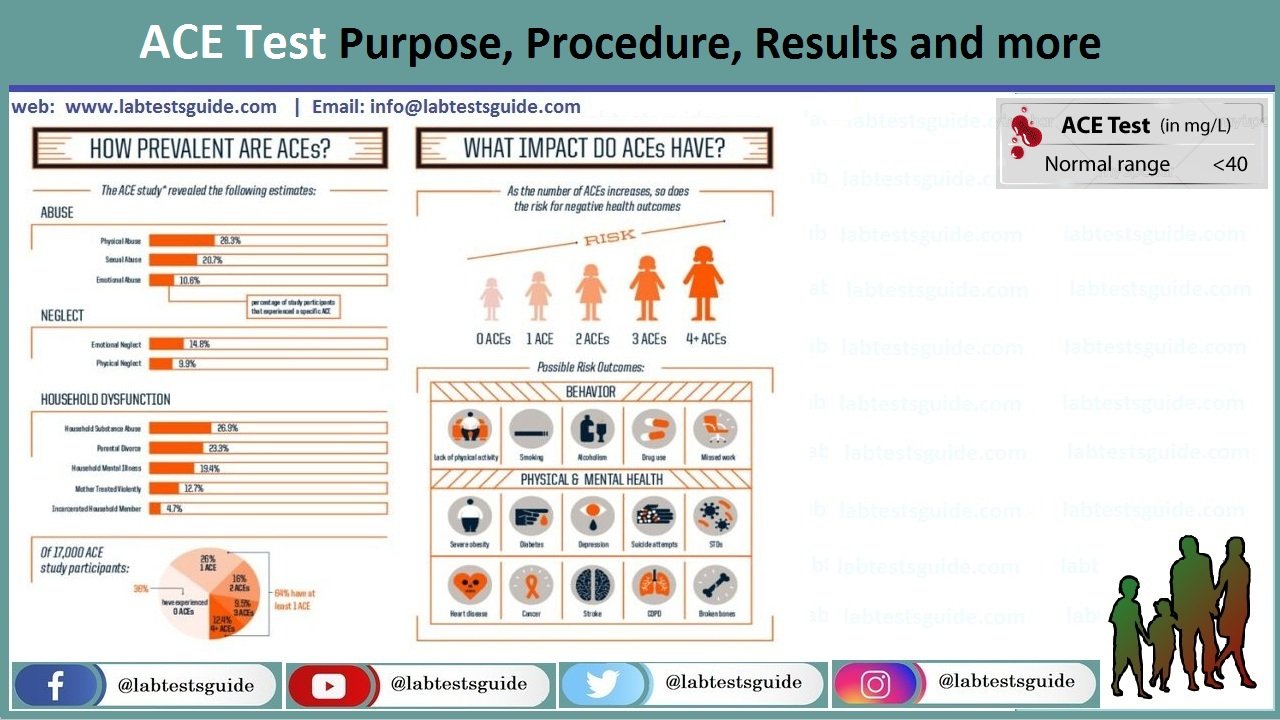
Most of the time we uses the ACE level test to monitor a disease called sarcoidosis. This condition causes inflammatory cells called granulomas to form in the body, leading to inflammation of the organs. Organs that can be affected by sarcoidosis include:
- lungs
- skin
- eyes
- lymph nodes
- liver
- heart
- spleen
When to get Tested:
- When you have granulomas that produce small bumps under the skin.
- When you have a lingering cough.
- When you have red watery eyes.
- When you have symptoms suggestive of sarcoidosis.
- Regularly when you have active sarcoidosis to monitor its course.
Other symptoms include:
- night sweats
- a loss of appetite
- swollen lymph nodes
- joint pain
- dry mouth
- nosebleeds
Sample Required:
Collection Container/Tube:
- Preferred: Serum gel
- Acceptable: Red top
- Submission Container/Tube: Plastic vial
- Specimen Volume: 1.5 mL
How to Prepare for the Test
Follow your health care provider’s instructions for not eating or drinking for up to 12 hours before the test. If you are on steroid medicine, ask your provider if you need to stop the medicine before the test, because steroids can decrease ACE levels. DO NOT stop any medicine before talking to your provider.
Reject Due To
| Gross hemolysis | Reject |
| Gross lipemia | Reject |
| Gross icterus | Reject |
Specimen Stability Information
| Specimen Type | Temperature | Time | Special Container |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum | Refrigerated (preferred) | 7 days | |
| Frozen | 180 days | ||
| Ambient | 24 hours |
Normal Values:
Normal Value of ACE : Upto 40 mg/l
High ACE Level Seen in:
- Cancer of the lymph tissue (Hodgkin disease)
- Diabetes mellitus
- Liver swelling and inflammation (hepatitis) due to alcohol use
- Lung disease such as asthma, cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or tuberculosis
- Kidney disorder called nephrotic syndrome
- Multiple sclerosis
- Adrenal glands do not make enough hormones (Addison disease)
- Stomach ulcer
- Overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism)
- Overactive parathyroid glands (hyperparathyroidism)
Low ACE Level Seen in:
- Chronic liver disease
- Chronic kidney failure
- Eating disorder called anorexia nervosa
- Steroid therapy (usually prednisone)
- Therapy for sarcoidosis
- Underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)
Related Articles:
Keywords: Serum Angiotensin Converting Enzyme, ACE Level, Serum ACE, ACE, Angiotensin-1-Converting Enzyme, Kinase II, Peptidylpeptide Hydrolase, SACE (Serum Angiotensin Converting Enzyme), Sarcoidosis, Serum Angiotensin Converting Enzyme,
RELATED POSTS
View all