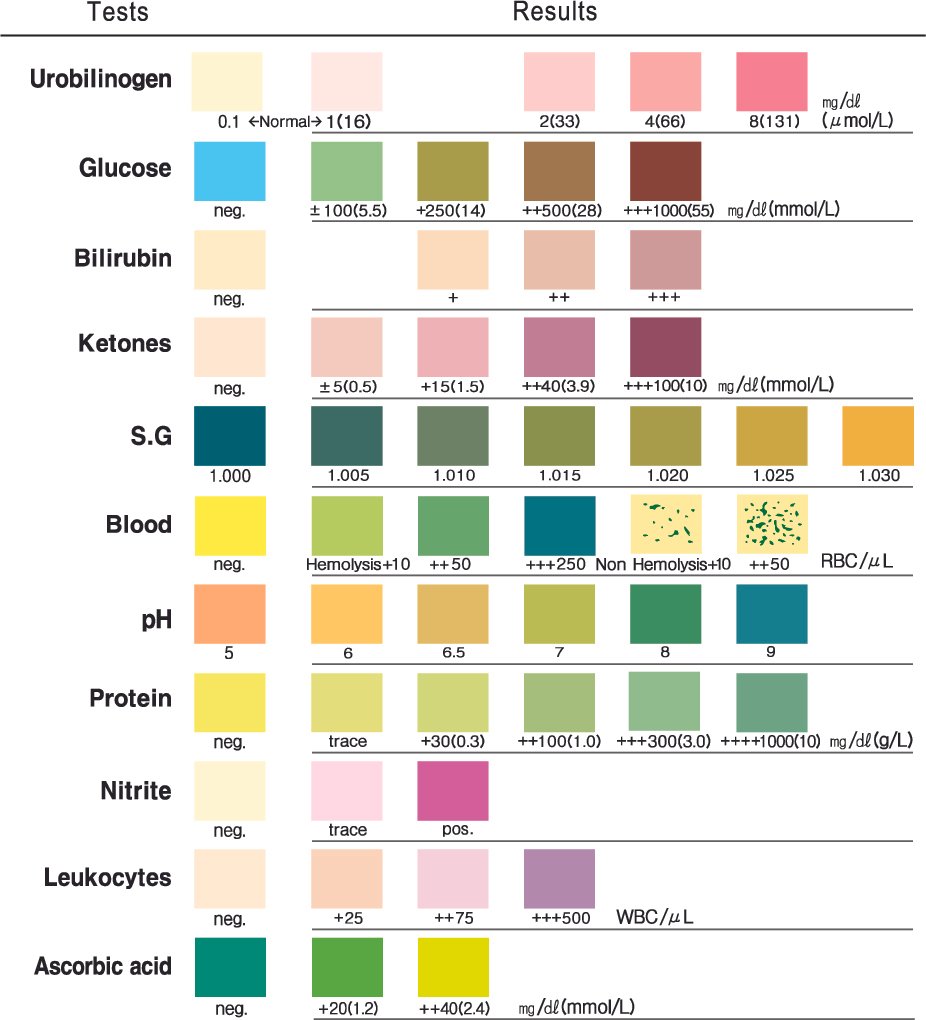
A bilirubin in urine test measures the levels of bilirubin in your urine. Bilirubin is a yellowish substance made during the body’s normal process of breaking down red blood cells. Bilirubin is found in bile, a fluid in your liver that helps you digest food.
A urinalysis is a test of your urine. A urinalysis is used to detect and manage a wide range of disorders, such as urinary tract infections, kidney disease and diabetes.
A urinalysis involves checking the appearance, concentration and content of urine. Abnormal urinalysis results may point to a disease or illness.

Also Known as: Urine Test, Urine Analysis , Urine CE, Urine C/E, UCE, Urinalysis
Test Panel: Physical properties, Chemical Tests, Dipstick Tests, Microscopic Examination
Type of urine samples:
- Random sample:
This is a diluted urine sample and may give an inaccurate interpretation of patient health. But is best to do microscopy to evaluate WBC or RBC. - First Morning sample:
This is the best sample for microscopy and urine analysis. This is the concentrated urine because of urine remained throughout the night in the urinary bladder. This will contains an increased concentration of analytes and cellular elements. Urine must have remained in the bladder for 8 hours is considered as the first-morning sample. - Urine for sugar (Postprandial 2 hours):
Postprandial 2 hours sample collected after 2 hours of high carbohydrate diet. - Midstream clean catch urine:
This sample is needed for the culture and sensitivity of urinary infection. The patient is advised to clean the urethra, then discard the first few mL of urine. Now midstream of the urine is collected in the sterile container. - 24 Hours of a urine sample
- In this case, discard the first urine and note the time.
- Now collect urine in the container for 24 hours and put the last sample in the container.
- Refrigerate the sample.
- This 24 hours samples are needed for measuring urea, creatinine, sodium, potassium, glucose, and catecholamines.
- Suprapubic collection of the urine sample:
This is done in the patients who cannot be catheterized and the sample is needed for culture. This sample is collected by the needle. - Catheter collection of urine:
This is done by patients who are bedridden and can not urinate. - Pediatric urine sample:
In infants, special collection bags are made adherent around the urethra. Then urine is transferred to a container.
Urinary Bilirubin :
A bilirubin in urine test measures the levels of bilirubin in your urine. Bilirubin is a yellowish substance made during the body’s normal process of breaking down red blood cells. Bilirubin is found in bile, a fluid in your liver that helps you digest food.
Why Get Tested:
Your health care provider may have ordered a bilirubin in urine test as part of your regular checkup, or if you have symptoms of liver disease. These symptoms include:
- Jaundice, a condition that causes your skin and eyes to turn yellow
- Dark-colored urine
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
When to get Tested:
your health care provider may order a bilirubin in urine test if you are at a higher risk for liver damage. Risk factors for liver disease include:
- Family history of liver disease
- Heavy drinking
- Exposure or possible exposure to hepatitis virus
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Taking certain medicines that can cause liver damage
Normal Range:
- Normally bilirubin is absent in the urine (0 to 0.02 mg/dL).
- Even traces indicate liver disease like hepatitis.
Sample Required:
- The sample is urine.
- The random sample can be taken.
Increased urine bilirubin is seen in:
- Hepatitis and liver diseases caused by infection or exposure to toxic agents ( cirrhosis ).
- obstructive biliary tract disease.
- Liver or biliary tract tumor.
- Septicemia.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Gallstones.
- Metastatic tumor in the liver.
- Drugs
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome.
- Rotor syndrome.
Urine Bilirubin / urobilinogen differential diagnosis
| Test | Normal | Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia | Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia | Hepatitis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urine bilirubin | negative | positive | negative | positive |
| Urine urobilinogen | positive / negative | positive (+++) | negative | positive (+++) |
Related Articles:
RELATED POSTS
View all