A urinalysis is a test of your urine. A urinalysis is used to detect and manage a wide range of disorders, such as urinary tract infections, kidney disease and diabetes.
A urinalysis involves checking the appearance, concentration and content of urine. Abnormal urinalysis results may point to a disease or illness.

Also Known as: Urine Test, Urine Analysis , Urine CE, Urine C/E, UCE, Urinalysis
Test Panel: Physical properties, Chemical Tests, Dipstick Tests, Microscopic Examination
Type of urine samples:
- Random sample:
This is a diluted urine sample and may give an inaccurate interpretation of patient health. But is best to do microscopy to evaluate WBC or RBC. - First Morning sample:
This is the best sample for microscopy and urine analysis. This is the concentrated urine because of urine remained throughout the night in the urinary bladder. This will contains an increased concentration of analytes and cellular elements. Urine must have remained in the bladder for 8 hours is considered as the first-morning sample. - Urine for sugar (Postprandial 2 hours):
Postprandial 2 hours sample collected after 2 hours of high carbohydrate diet. - Midstream clean catch urine:
This sample is needed for the culture and sensitivity of urinary infection. The patient is advised to clean the urethra, then discard the first few mL of urine. Now midstream of the urine is collected in the sterile container. - 24 Hours of a urine sample
- In this case, discard the first urine and note the time.
- Now collect urine in the container for 24 hours and put the last sample in the container.
- Refrigerate the sample.
- This 24 hours samples are needed for measuring urea, creatinine, sodium, potassium, glucose, and catecholamines.
- Suprapubic collection of the urine sample:
This is done in the patients who cannot be catheterized and the sample is needed for culture. This sample is collected by the needle. - Catheter collection of urine:
This is done by patients who are bedridden and can not urinate. - Pediatric urine sample:
In infants, special collection bags are made adherent around the urethra. Then urine is transferred to a container.
Urine PH
A urine pH level test is a test that analyzes the acidity or alkalinity of a urine sample. It’s a simple and painless test. Many diseases, your diet, and the medicines you take can affect how acidic or basic your urine is. For instance, results that are either too high or low can indicate the likelihood that your body will form kidney stones. If your urine is at an extreme on either the low or high end of pH levels, you can adjust your diet to reduce the likelihood of painful kidney stones.
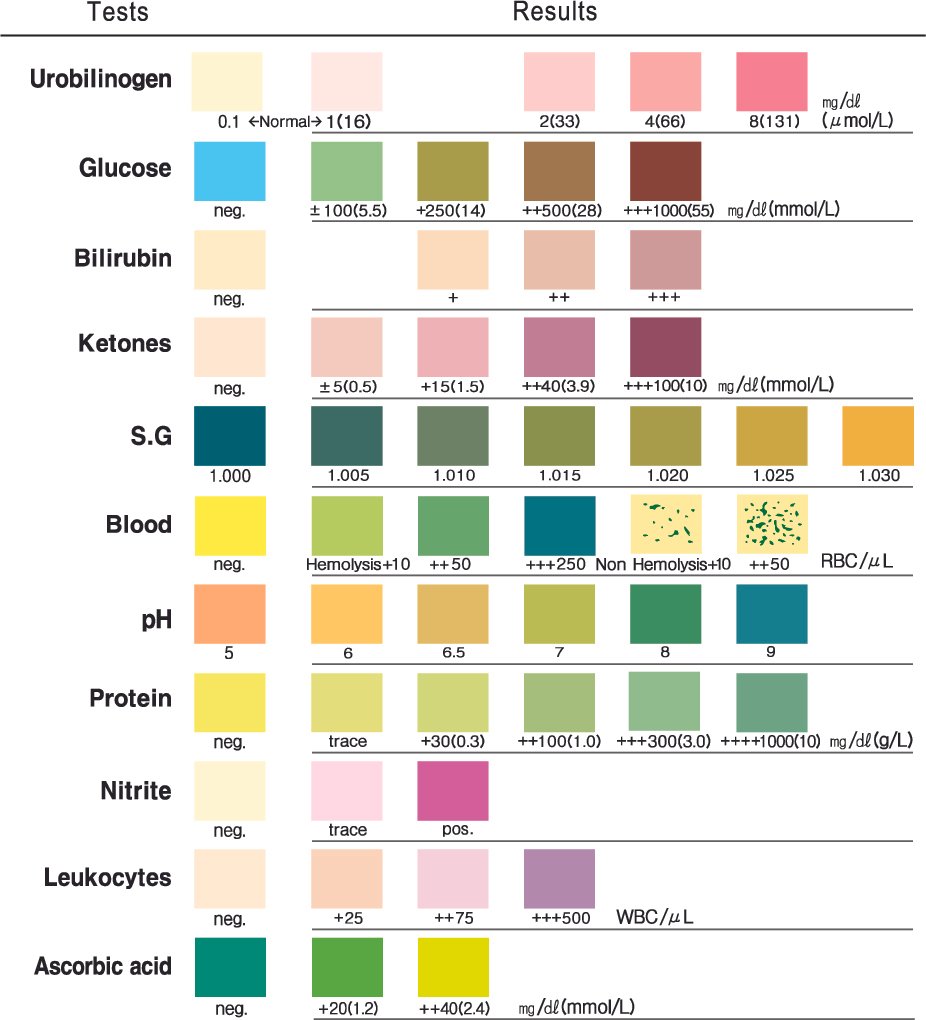
Why Get Tested:
Prior to testing, your doctor may ask you to stop taking certain medications known to affect your urine pH. Examples of these drugs include:
- acetazolamide, used to treat glaucoma, epilepsy, and other disorders
- ammonium chloride, used in some cough medicines
- methenamine mandelate, used to treat urinary tract infections
- potassium citrate, used to treat gout and kidney stones
- sodium bicarbonate, used to treat heartburn and acid indigestion
- thiazide diuretics, used to treat high blood pressure and to reduce the risk of stroke and heart attacks
- pH tells the systemic acid-base disorder:Is it metabolic?
- Or Respiratory.
- Renal tubular acidosis.
- pH is used to identify the type of crystals.
- pH is important to manage diseases, bacteriuria, renal calculi, and drug therapy.
Normal Range:
The average value for urine pH is 6.0, but it can range from 4.5 to 8.0. Urine under 5.0 is acidic, and urine higher than 8.0 is alkaline, or basic.
Hihg Urinary Ph is Seen in:
If a person has a high urine pH, meaning that it is more alkaline, it might signal a medical condition such as:
- kidney stones
- urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- kidney-related disorders
High Urinary Ph is Seen in:
If a person has low urine pH, meaning that it is more acidic, it might indicate a medical condition such as:
Causes of acid and alkaline urine:
| Alkaline urine | Acidic urine |
|---|---|
| Vomiting | Diabetes mellitus |
| Hyperventilation | Starvation |
| Vegetarian diet | Diarrhea |
| Old specimen | Dehydration |
| Renal tubular acidosis | High protein diet |
| Urease-producing bacteria | Emphysema |
| Acid producing bacteria | |
| Cranberry juice | |
| Medicines |
pH urine role in renal calculi:
- Renal stone formation depends upon urine pH.
- Calcium phosphate, calcium carbonate, and magnesium phosphate stones form in alkaline pH, so keep the urine acidic to prevent their formation.
- Uric acid, calcium oxalate, and cystine, forms in acidic urine, to prevent their formation, keep the urine pH alkaline.
pH urine role in drug therapy:
- Neomycin, kanamycin, and streptomycin are effective in alkaline urine.
- Salicylate intoxication keeps the urine pH alkaline.
- Sulfa therapy forms crystals and these can be prevented by keeping urine pH alkaline.
pH urine role in diseases:
- keep urine pH acidic during :
- The treatment of urinary tract infection.
- In persistent bacteriuria.
- In renal calculi which develop in alkaline urine.
Diet effect on urine pH:
- Vegetarian diet, citrus fruits keep urine alkaline.
- Diet rich in protein (meat), keeps urine acidic.
- Cranberry juice keeps urine acidic and some believe it as a remedy for UTI.
Acidic foods include:
- Grains
- Fish
- Sodas
- High-protein foods
- Sugary foods
Alkaline foods include:
- Nuts
- Vegetables
- Most fruits
Related Articles:
RELATED POSTS
View all
