A differential blood count gives the relative percentage of each type of white blood cell and also helps to reveal abnormal white blood cell populations (eg, blasts, immature granulocytes, and circulating lymphoma cells in the peripheral blood).
Also Known As: Leukocyte Differential Count, Peripheral Differential, WBC Count Differential, Diff ,Blood Differential, Differential Blood Count, DLC
Test Panel: Hemoglobin, Red Blood Cells (RBC), HCT, MCV, MCH, MCHC, Platelets Count, White Blood Cells (WBC), DLC, ESR
Why and When to get Tested:
- It is a general screening test and gives tremendous information’s about the hematological system and another organ system.
- It will differentiate between acute or chronic infection.
- It will diagnose and type the anemia.
- It will diagnose any type of leukemia.
- These are easy, inexpensive and rapid to perform.
- It will find any abnormality in the count of platelets.
Sample Rewuired:
- The best sample is blood in EDTA.
- Also, prepare fresh peripheral blood smear.
- This is inexpensive, easy to perform and rapidly done as a screening test.
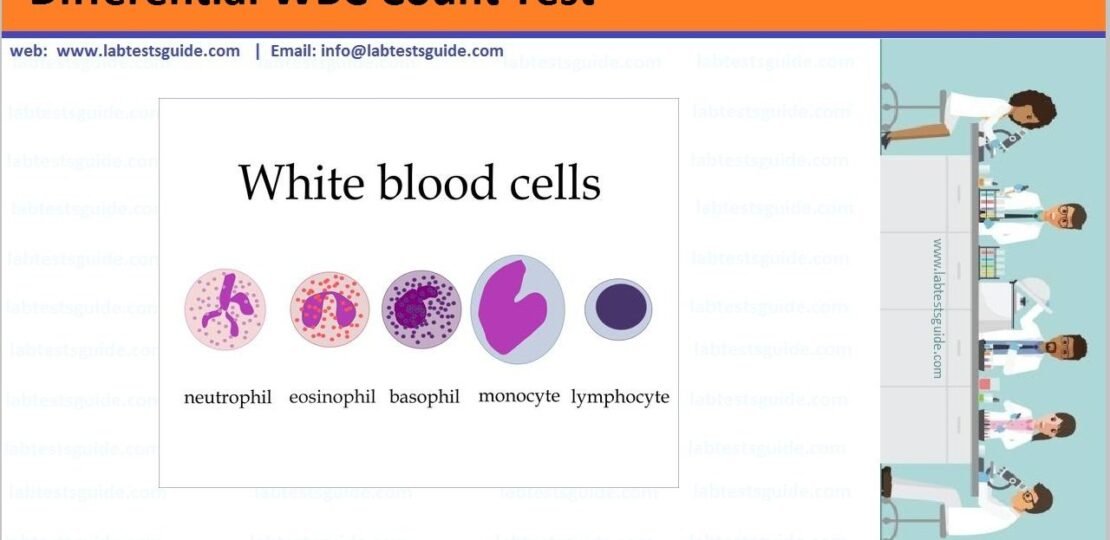
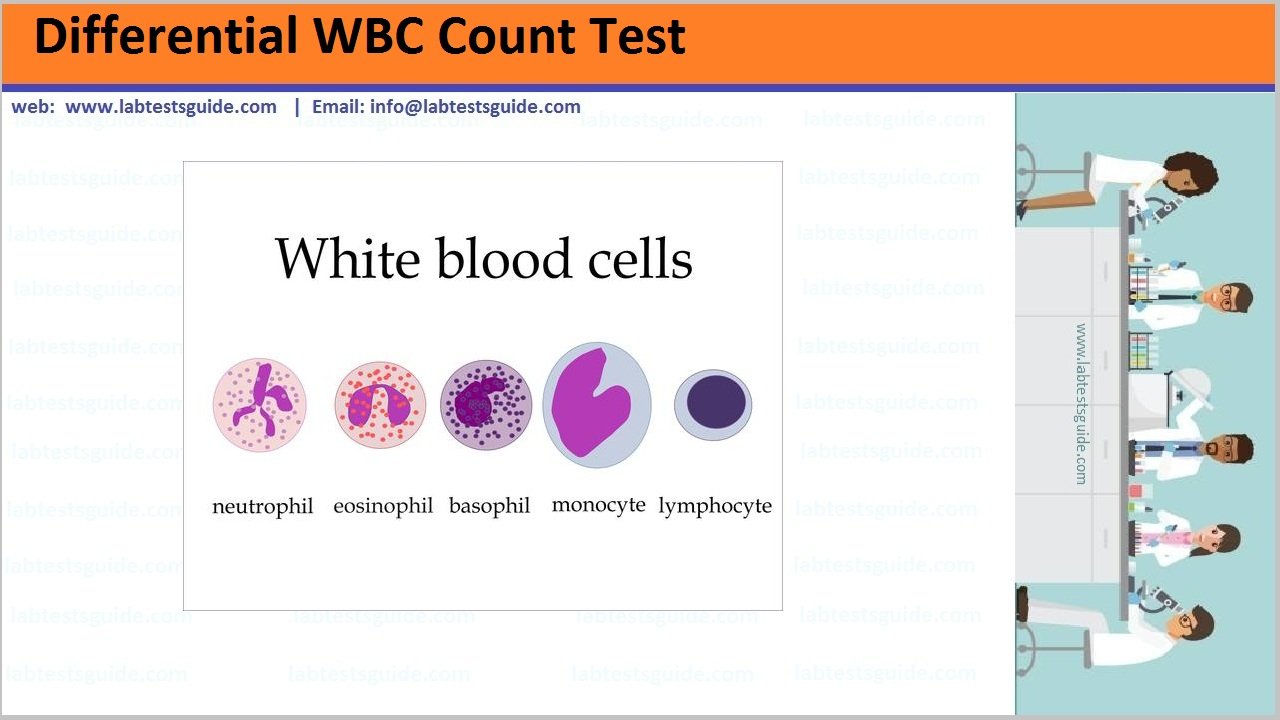
Types of WBC:
have five types of white blood cells:
Referance Ranges:
| Test Name | Male | Female |
| Neutrophils (Poly) | 40 – 75 % | 30-75 g/dl |
| Lymphocytes | 20 – 50 % | 20 – 50 % |
| Monocytes | 2- -10 % | 2- -10 % |
| Eosinophils | 1- 6 % | 1- 6 % |
| Basophils | 0.3 – 1 % | 0.3 – 1 % |
Neutrophils increased in:
- Infections.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Stress.
- metabolic diseases.
- Inflammations.
Neutrophil Decreased in:
- In radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
- Infections.
- hypersplenism.
- Folic acid or B12 deficiency.
- Hepatic diseases.
- Drugs
- collagen vascular diseases.
Eosinophils increased in:
- Allergy.
- Parasitic infestation.
- Skin disorders.
- Neoplastic diseases like Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- Collagen vascular diseases.
Eosinophil Decreased in:
- Cushing’s syndrome.
- Stress.
Lymphocytes increased in:
- Chronic infections.
- Lymphocytic leukemia.
- In immune diseases e.g Ulcerative colitis.
Lymphocyte Decreased in:
- Chronic debilitating illness.
- Immune-deficiency.
Monocytes increased in:
- Infections.
- Collagen vascular diseases.
- Carcinoma.
- monocytic leukemia.
- Lymphoma.
Basophils Increased in:
- Chronic myelocytic leukemia.
- polycythemia vera.
- Hodgkin’s disease.
- In some anemias.
Basophil Decreased in:
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Stress.
- ovulation.
Note: please see more information in peripheral and RBCs smear.
Related Articles:
RSS Error: https://www.labtestsguide.com/category/tests/feed is invalid XML, likely due to invalid characters. XML error: > required at line 490, column 16
RELATED POSTS
View all

